Abstract
Background:
Multiple Myeloma (MM) accounts for 1.6% of all cancers and 5-10% of hematologic malignancies in the United States. Novel therapeutic agents have raised the overall survival from 1-2 years to 7-8 years with meaningful improvement in quality of life. Ongoing clinical trials have significantly contributed to the favorable disease outcomes, however many of these interventions still remain unknown to clinicians. The significance of citation analysis lies in the fact that clinicians often modify their management strategy based on research published in high impact journals. In this article, our main objective is to assist medical professionals working in the field to identify the most influential research published on MM.
Materials and methods:
We conducted a bibliographic analysis on the Web of Science (WOS). Included journals were those listed in the Science Citation Index Expanded, without specific restrictions on the journals. We retrieved the articles for analysis by typing "Multiple Myeloma" into WOS search box and conducted this data search in Title setting with application of English language filter on 07-25-2017.
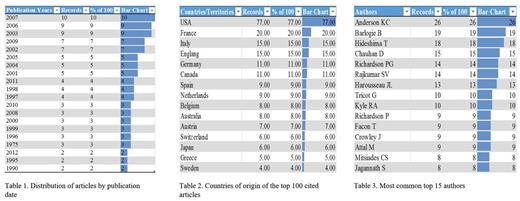
Results: We identified 27,718 articles published between 1901 and 2017, ranked the articles on the basis of citation frequency from highest to lowest and thereafter shortlisted the top 100 cited articles. The most cited article received 2404 citations. Top 100 cited articles were published between 1990 and 2007. In our analysis, we found that highest number of articles were published in the year 2007 (Table 1). 44 out of 100 articles were published in journals with impact factor (IF) greater than 20. The journal with highest number of publications (36%) was BLOOD (IF 13.16). The country with leading number of publication on MM was the United States of America (77%), followed by France (20%), Italy (15%), and the United Kingdom (15%) (Table 2). The production of these 100 articles originated from 50 centers, the most significant contributors out of which were VA Boston Healthcare system and Harvard University each with 36% of total articles, followed by Dana-Farber with 34% of the total articles. Anderson KC., was found to be most frequently cited common author with his contributions amounting up to 26% of the total (Table 3). Maximum studies were found to be categorized under the title of hematology (40%), followed by general internal medicine (29%) and oncology (27%).
Discussion:
MM research has gone through milestones in areas including disease staging, pathogenesis and management. Seven articles focused on staging, 29 on disease pathogenesis and 51 on treatment. Two of the top ten most cited articles were aimed at staging. Clinical staging was proposed by Durie BGM et al., although the most cited article in our list is no longer the primary staging system. Current classification of MM is based on revised international staging system and disease cytogenetics. Second most frequently encompassed category was disease pathogenesis. Over the years, understanding of pathogenesis has laid the foundation for development of novel therapeutic agents. Among the top 100 cited articles, only 7 studies were focused on bortezomib containing regimens, whereas none of them included carfilzomib or Ixazomib based novel therapeutic regimens. This shows that articles with high frequency of citations mostly consist of early-published articles. Among the top 100 list, only two articles were from 2012 (latest year on the list). To capture important and latest research, a second search was carried out with strategy to limit articles published during last five years.
Conclusion:
A bibliographic analysis of top cited articles published focused on disease staging, pathogenesis and management. Search limited to last five years (2012-2017) portrayed different results from our original search. None of the studies in the last 5 years list were included in the original list due to less number of total citations received. Recent studies focused on latest developments including therapeutic agents such as novel proteasome inhibitors (carfilzomib, Ixazomib) and monoclonal antibodies (daratumumab, eculizumab) among others. Hence we can infer that top cited article set the stage with deeper understating about MM and helped make solid foundations for the latest developments in the field. We continue to expect ground breaking discoveries be shared through medical scientific literature.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal